Leave Your Message
Industrial Silicon plays a pivotal role in various technological advancements, serving as a foundational element in numerous applications that drive modern industry. From electronics to energy, the versatility of Industrial Silicon has made it an essential material in the manufacturing of semiconductors, solar cells, and silicon-based products. Understanding the properties and applications of this key material is crucial for professionals in sectors ranging from engineering to environmental science.
As the demand for sustainable solutions and high-performance materials continues to rise, gaining insight into the characteristics and utilization of Industrial Silicon becomes increasingly important. This article presents ten essential tips to enhance your comprehension of Industrial Silicon and its multifaceted applications. By exploring its production processes, innovative uses, and the implications for future technologies, readers will develop a well-rounded grasp of how Industrial Silicon influences contemporary and emerging industries. With this knowledge, professionals can better navigate the complexities of the field and make informed decisions that leverage the potential of this remarkable material.

Industrial silicon, primarily composed of silicon with varying purity levels, plays a critical role in a multitude of industries, including electronics, renewable energy, and metallurgy. Silicon's atomic structure, comprising 14 electrons, allows it to form various bonds, making it a versatile material. The intrinsic properties of silicon encompass high thermal conductivity, moderate electrical conductivity, and excellent durability. These characteristics make it ideal for use in semiconductors, where it facilitates the control of electrical current and is vital in the production of solar cells, transistors, and other electronic components.
Understanding the composition of industrial silicon involves recognizing the distinctions between various silica forms, such as metallurgical and chemical-grade silicon. Metallurgical silicon, typically around 98% pure, is utilized primarily in the production of aluminum alloys and silicone products, while higher purity silicon (up to 99.9999%) is essential for advanced applications in electronics and solar technology. The methods of refining silicon, including carbothermic reduction and purification processes, significantly influence its properties and efficacy in specific applications.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-quality industrial silicon will become more pronounced, emphasizing the need for innovation in silicon processing and its applications.
The production of industrial silicon involves several key manufacturing processes, each essential to obtaining the high purity required for various applications. The process typically begins with the purification of silica, which is often sourced from quartz sand. This silica is then reduced to silicon through high-temperature chemical reactions in an electric arc furnace. According to the IC Insights report, the global market for silicon is projected to reach $28.9 billion by 2027, highlighting the critical role this material plays in semiconductor manufacturing and renewable energy technologies.
Once the silicon is purified, the next step can involve alloying, where silicon is combined with other elements to improve its properties for specific uses. For instance, silicon-aluminum alloys are commonly utilized in automotive parts and aerospace applications due to their lightweight and strength characteristics. A study by MarketsandMarkets indicates that the demand for silicon-based alloys is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2021 to 2026. This signifies not only the versatility of industrial silicon but also the ongoing innovations in manufacturing practices aimed at enhancing sustainability and efficiency in production. As industries continue to seek materials that meet environmental standards and performance requirements, the significance of understanding the manufacturing processes behind industrial silicon cannot be overstated.
| Process | Description | Applications | Key Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Purification | Removal of impurities from raw silicon. | Semiconductors, Solar Cells | Purification Furnace, Chemical Reactors |
| Silicon Alloying | Combining silicon with other metals to enhance properties. | Aluminum Alloys, Steel Production | Alloying Furnaces, Melting Units |
| Polysilicon Production | Production of high-purity silicon material for solar cells. | Solar PV Modules | Chemical Vapor Deposition Reactors |
| Ingot Casting | Casting silicon into blocks for further processing. | Semiconductor Manufacturing | Casting Machines, Crucibles |
| Wafer Fabrication | Slicing ingots into thin wafers for electronics. | Microprocessors, Photovoltaics | Wafer Saws, Lapping Machines |
Industrial silicon plays a crucial role in various modern technologies, especially in the fields of electronics and solar energy. In electronics, silicon is the fundamental material for semiconductor devices, which are integral to the functionality of computers, smartphones, and numerous other electronic gadgets. Its excellent electrical conductivity, coupled with its ability to be easily manipulated into various forms, makes silicon essential for the production of transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits.
When it comes to solar energy, industrial silicon is used to manufacture photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. The efficiency of solar panels largely depends upon the quality and purity of silicon utilized. In this realm, understanding how to optimize silicon for better energy conversion and cost-effectiveness is vital.
Tip: Always prioritize purity when selecting silicon for electronics; impurities can lead to a significant drop in device performance.
Tip: For solar energy applications, consider silicon's crystallinity; monocrystalline silicon generally offers higher efficiency compared to polycrystalline alternatives, making it a better choice for maximizing output in space-constrained installations.
The applications of industrial silicon continue to expand, driving innovations that power our technology-driven world and promote sustainable energy solutions.
This chart illustrates the various applications of industrial silicon in electronics and solar energy, showcasing the relative proportions of each application within the industry.
Silicon plays a pivotal role in the semiconductor industry, serving as the foundational material for various electronic devices. In 2020, the global semiconductor market was valued at approximately $440 billion, with silicon-based products dominating the landscape. According to a report by Gartner, silicon wafers constitute about 37% of the total semiconductor market, reflecting their essential role in producing integrated circuits, which are the backbone of modern technology.
The applications of silicon in the semiconductor industry are vast, ranging from microprocessors in computers to power semiconductors used in renewable energy systems. The demand for silicon is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2021 to 2028, driven by advancements in technology such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. The unique electrical properties of silicon, combined with its abundance and cost-effectiveness, make it an ideal choice for manufacturers aiming to enhance performance while reducing production costs. Thus, understanding the characteristics of industrial silicon is essential for anyone looking to engage with or invest in the semiconductor industry.
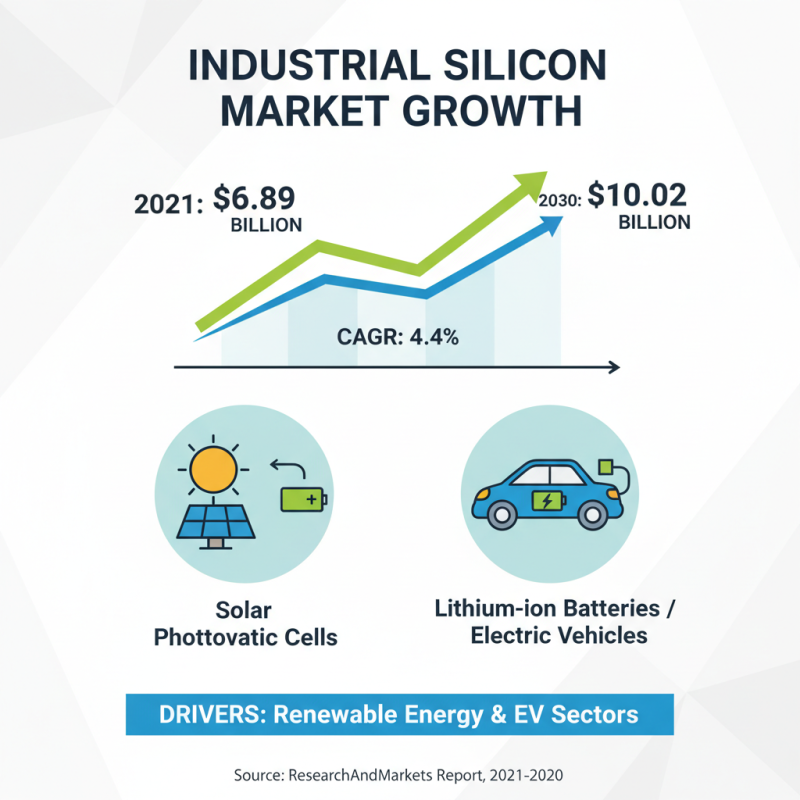
The industrial silicon market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of technological advancements and increasing demand from various sectors. According to a recent market analysis report from ResearchAndMarkets, the global industrial silicon market was valued at approximately USD 6.89 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 10.02 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 4.4% during the forecast period. This surge can largely be attributed to the rising adoption of silicon in the production of solar photovoltaic cells and lithium-ion batteries, which are essential components in the renewable energy and electric vehicle sectors.
In addition to renewable energy, the electronics and semiconductor industries are also boosting the industrial silicon market. Data from a report by MarketsandMarkets highlights that the semiconductor segment is projected to witness substantial growth due to the increasing need for high-performance materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and power levels. As industries continue to innovate and seek more efficient materials for energy conversion and storage, the demand for high-purity silicon is anticipated to escalate. Moreover, sustainability initiatives and the transition towards green technology are further positioning industrial silicon as a key player in the global market landscape for the coming years.






