Leave Your Message
In the landscape of industrial applications, Silicon Iron has emerged as a pivotal material, celebrated for its excellent magnetic properties. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in metallurgical engineering, once stated, "Silicon Iron opens new avenues for energy-efficient solutions." Her words encapsulate the transformative potential of this alloy.
Silicon Iron's unique composition significantly enhances performance in electrical and magnetic applications. Industries increasingly rely on it for transformers, electric motors, and generators. The magnetic permeability of Silicon Iron makes it essential for creating efficient energy systems. However, challenges remain in optimizing its manufacturing process to meet rising demands.
As industry continues to evolve, the use of Silicon Iron must be scrutinized and adapted. It is crucial to reflect on the environmental impact and explore sustainable sourcing. The journey towards effective Silicon Iron applications is ongoing, urging engineers and manufacturers to innovate while considering these critical aspects.


Silicon iron is a crucial alloy in various industries. Its unique properties stem from its composition. Typically, silicon iron contains 15-90% silicon with iron as the main component. This blend allows for improved electrical and thermal conductivity. Reports indicate its use in transformers enhances energy efficiency by up to 5%. This percentage can significantly affect operational costs in power systems.
In addition to electrical applications, silicon iron shines in manufacturing. It exhibits excellent magnetic properties, making it ideal for components like inductors and motors. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, components made from silicon iron have a higher saturation flux density. This trait allows for compact designs and reduced weight. However, achieving the right balance in composition is challenging. Variability in production can lead to inconsistencies, which can compromise performance.
Finally, silicon iron’s mechanical properties present limitations. While it is ductile, excessive silicon can make it brittle. This brittleness requires careful consideration during manufacturing processes. Industries must prioritize quality control to minimize defects. As demand grows, so does the need for optimized silicon iron formulations. Striking the right balance is key to achieving the best results.
Silicon iron, a strategic material in electrical engineering, finds diverse applications, particularly in motors. The unique properties of silicon add magnetic performance and enhance efficiency. Higher silicon content leads to increased electrical resistivity, reducing energy loss. This makes silicon iron an ideal choice for transformer cores and inductors.
In motor applications, silicon iron promotes effective magnetic flux. It contributes to lighter and more compact designs. These motors can run more efficiently due to lower hysteresis losses. However, the production process can be challenging. Achieving the right silicon level requires precise control and quality management.
While the advantages are clear, there are pitfalls too. Not all silicon iron variants suit every application. Engineers need to thoroughly test and understand specific requirements. Miscalculations can lead to performance gaps, wasting time and resources. Awareness of these challenges is vital in optimizing silicon iron usage in industry.
Silicon iron alloys are pivotal in enhancing the magnetic properties of transformers. These alloys typically contain between 3% to 6.5% silicon, significantly improving electrical resistivity. This change helps reduce energy losses during operation. Research by the International Electrotechnical Commission has revealed that transformers made with silicon iron can achieve efficiency levels exceeding 98%.
The increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions places pressure on manufacturers. While silicon iron alloys offer improved performance, their production requires careful balance. Excessive silicon can lead to brittleness, complicating processing. Thus, industry experts often recommend rigorous quality control measures during alloy production to avoid these pitfalls. In fact, a study released in the Journal of Magnetism highlighted that inconsistencies in silicon content can diminish the magnetic saturation levels significantly.
Moreover, the global transformer market is projected to grow, reaching over $70 billion by 2027. This trend underscores the need for advanced materials like silicon iron. However, challenges exist, notably in sourcing high-purity silicon. As industries strive for innovation, continuous research into enhancing alloy properties remains crucial. Maintaining this focus could ensure stronger performance in future transformer technologies.
Silicon iron is increasingly important in various industrial applications. The demand for this material is on the rise, driven by advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. Industries such as automotive and electronics are integrating silicon iron into their production lines. This integration improves the efficiency of electromagnetic components, making it a preferred choice among manufacturers.
However, the supply chain presents challenges. The extraction and processing of silicon iron can be inconsistent. Fluctuations in resource availability impact production schedules. Moreover, some manufacturers struggle to adapt to the new market trends. They may not have the resources to innovate or scale effectively. This creates a gap between supply and demand, affecting overall market stability.
As a result, companies need to rethink their strategies. Investing in sustainable practices may mitigate some supply issues. Collaborating with suppliers can create a more reliable sourcing process. Flexibility in production methods is crucial as industries evolve. Staying informed about market trends will help businesses navigate this complex landscape. The future of silicon iron in manufacturing depends on these adaptive strategies.
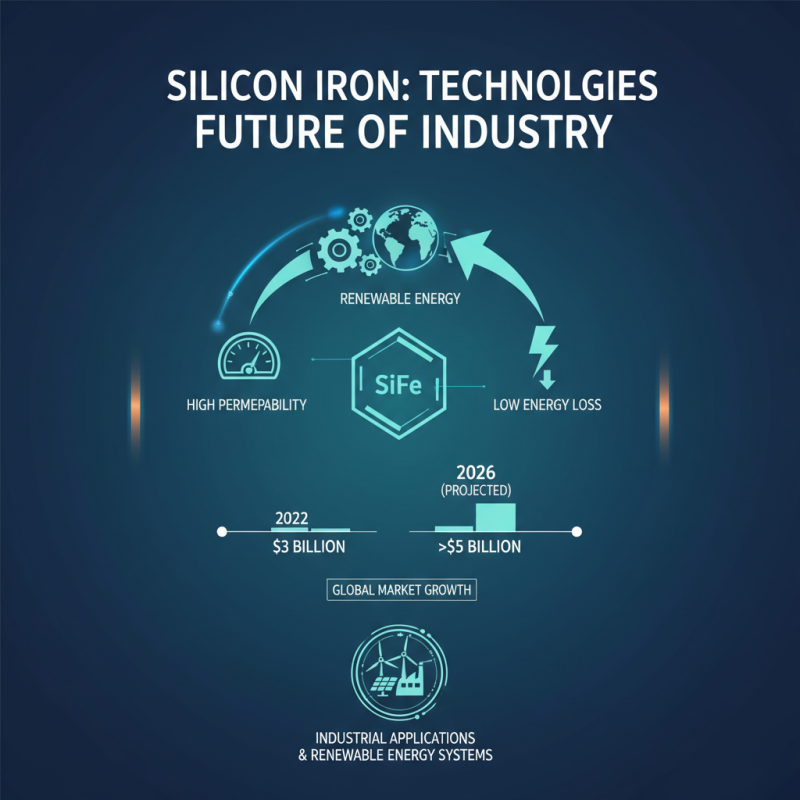
The future of silicon iron technologies in industrial applications looks promising. Data from the International Energy Agency indicates that the demand for silicon iron in renewable energy systems is increasing rapidly. In 2022, the market for silicon iron reached approximately $3 billion, with projections showing it could exceed $5 billion by 2026. Industries are considering silicon iron for its high permeability and low energy loss.
Innovations in processing techniques are transforming silicon iron's performance. Recent reports highlight methods such as rapid solidification and advanced alloying, which can improve magnetic properties significantly. Some manufacturers claim enhancements of up to 15% in efficiency for electrical steel applications. However, these improvements are not universally achievable. Factors like initial material quality vary across suppliers, affecting consistency and end performance. Data suggests that smaller manufacturers may struggle to reach these standards, presenting a significant barrier.
Additionally, researchers are exploring novel combinations of elements to enhance silicon iron's capabilities. This exploration could lead to tailored materials for specific industrial needs. However, navigating these advancements requires careful consideration. Balancing cost and quality remains a challenge. Some companies may prioritize low-cost options, sacrificing performance. Such decisions can lead to inefficiencies down the line, potentially undermining technological advancements. Overall, the evolution of silicon iron technology is tightly linked to both innovation and market dynamics, catalyzing a shift in industrial applications.






