Leave Your Message
Silicon Carbide Heating Elements have emerged as a revolutionary solution in the field of industrial heating. These advanced heating components, made from a compound of silicon and carbon, offer superior performance under high-temperature conditions, making them ideal for a variety of applications ranging from furnaces to semiconductor manufacturing. As Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in materials science, states, "The unique properties of Silicon Carbide allow for efficient energy transfer and enhanced durability, which are critical in today's demanding industrial environments."
Understanding how a Silicon Carbide Heating Element works involves exploring its structural and thermal characteristics. Unlike traditional heating elements, Silicon Carbide can withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining its integrity, resulting in significant energy savings and reduced maintenance costs. The element operates by converting electrical energy into thermal energy through resistive heating, delivering consistent and reliable performance. As industries strive for higher efficiency and sustainability, the role of Silicon Carbide Heating Elements is becoming increasingly prominent, providing innovative solutions that meet modern energy demands.
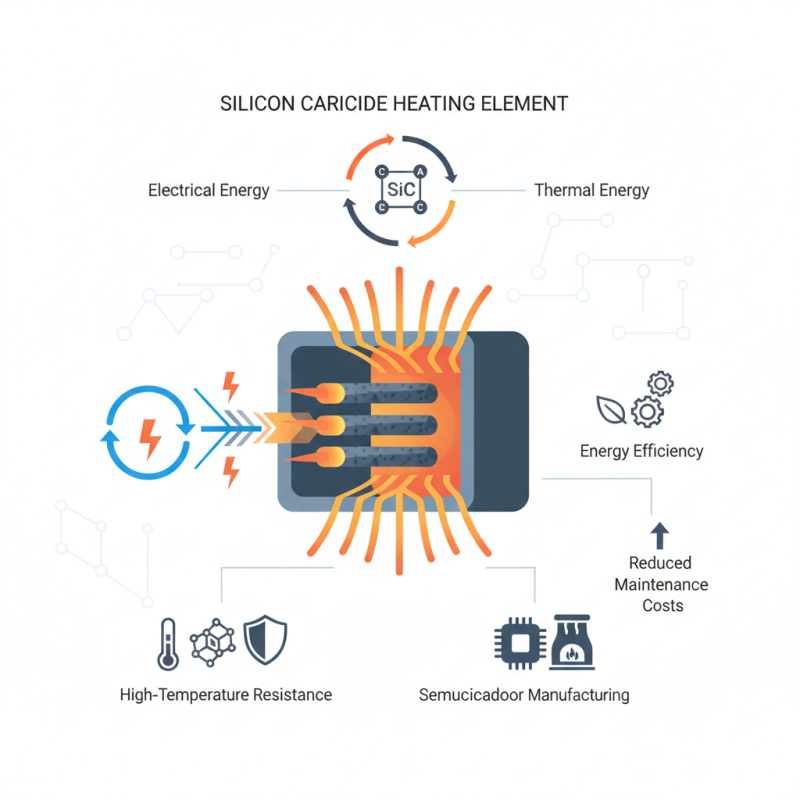
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound made of silicon and carbon, known for its exceptional properties that make it a preferred choice in various high-temperature applications. SiC is characterized by its high thermal conductivity, excellent thermal shock resistance, and a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which makes it incredibly stable under heat. According to a report by Technavio, the global silicon carbide market is projected to witness significant growth, as industries seek materials that can withstand extreme conditions. This growth highlights the unique ability of SiC to perform reliably in high-temperature furnaces, electric vehicles, and other demanding environments.
The unique properties of silicon carbide extend beyond thermal performance. SiC demonstrates outstanding electrical properties, including high breakdown voltage and minimal electron mobility, which makes it an excellent semiconductor material. Industry reports have noted that the efficiency of power devices made from SiC can exceed that of traditional silicon-based devices by up to 30%. This advantage allows for reduced energy loss in electrical applications, driving the adoption of silicon carbide heating elements in modern technology.
Tips: When considering silicon carbide heating elements, it's essential to assess the specific application requirements, including operating temperature and thermal cycling conditions. Opting for a SiC element can enhance the efficiency and longevity of heating systems, ultimately leading to lower energy costs and improved performance in demanding applications. Additionally, proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the lifespan of these heating elements, so always follow industry best practices.
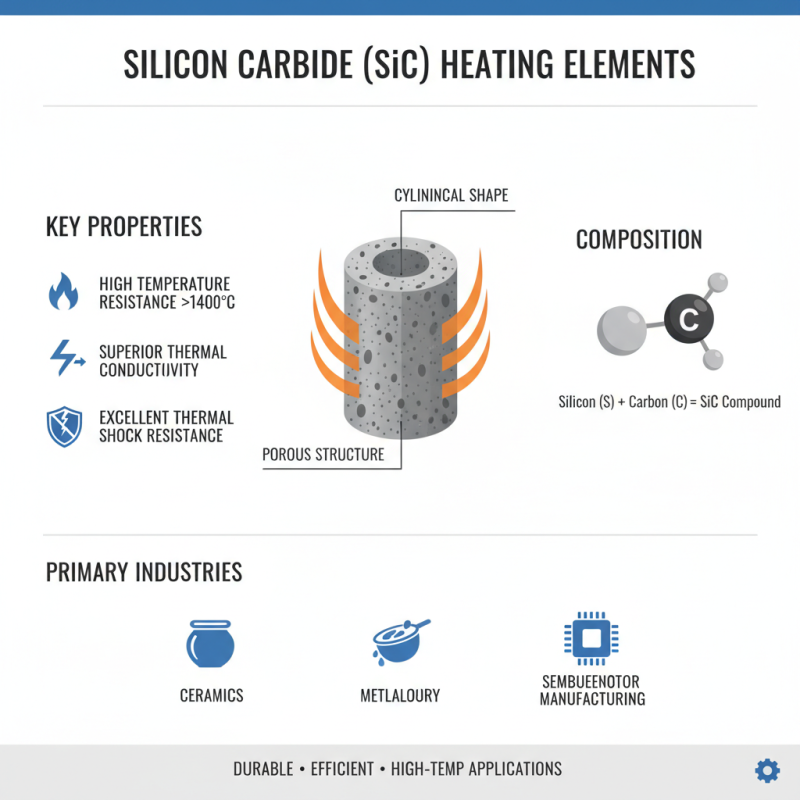
Silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are renowned for their durability and efficiency in high-temperature applications. Understanding their structure is key to appreciating how they function. SiC is a compound made from silicon and carbon, offering superior thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock compared to other materials. These heating elements typically consist of a cylindrical shape with a porous structure that promotes effective heat distribution. The unique crystalline configuration of SiC allows it to withstand temperatures exceeding 1400°C, making it ideal for industries such as ceramics, metallurgy, and semiconductor manufacturing.
The performance of silicon carbide heating elements can be significantly enhanced by focusing on their design. Recent industry reports indicate that properly engineered SiC elements exhibit up to a 30% increase in efficiency compared to older materials. Additionally, the use of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as sintering and doping, allows for tailored electrical resistance and thermal properties. This level of customization leads to reduced energy consumption and improved operational lifetimes, further emphasizing the advantages of integrating SiC heating technology.
Tips: When selecting silicon carbide heating elements for specific applications, consider factors like operational temperature range and the type of environment they will operate in. Regular maintenance checks can help maximize efficiency and extend the lifespan of these heating elements. Moreover, collaborating with experienced engineers can provide insights into optimal configurations for unique industrial requirements, ensuring the best performance.
Silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are renowned for their ability to withstand high temperatures and provide efficient energy transfer within various industrial applications. These heating elements function through the process of resistive heating, where the electric current passes through the silicon carbide material and encounters resistance, resulting in the generation of heat. The unique properties of SiC allow it to operate at temperatures reaching up to 1,600°C (2,912°F), making it a critical component in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing and metal processing.
The operation of a silicon carbide heating element involves its structure, which typically consists of a dense and durable hexagonal crystal lattice. This design not only enhances its thermal conductivity but also ensures uniform heat distribution across the element's surface. According to a report published by the International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, silicon carbide heating elements exhibit a significant energy efficiency rate of up to 93%, due to their ability to rapidly reach operating temperatures and maintain them without excessive energy loss. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in reducing operational costs for industries reliant on high-temperature processes, allowing for both energy savings and optimized production capabilities.
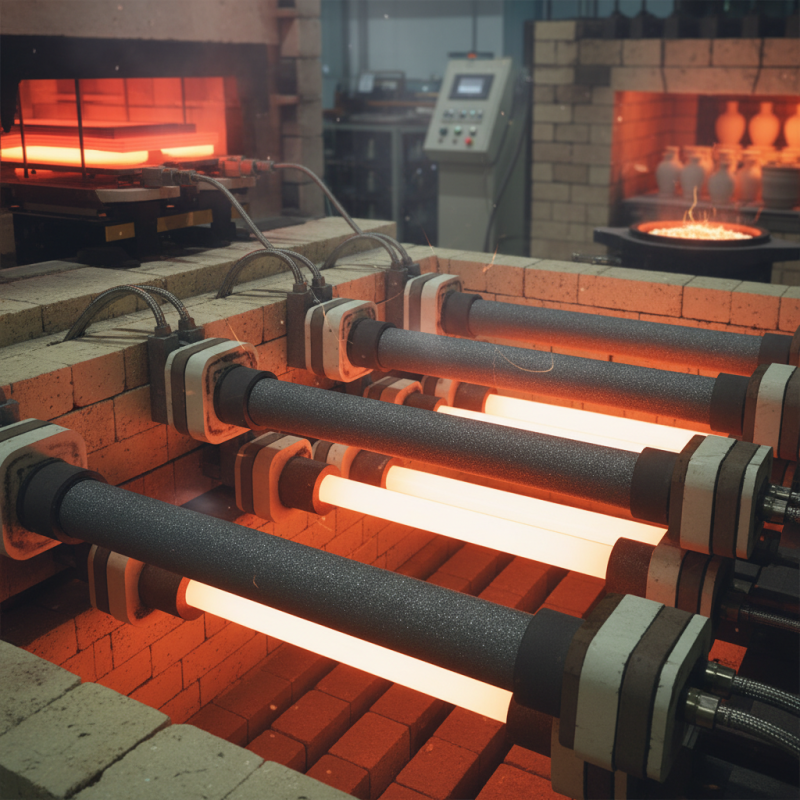

Silicon carbide heating elements are increasingly utilized in various industrial applications due to their unique properties. These elements are known for their ability to withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 1,600 degrees Celsius, making them ideal for processes that require intense thermal energy. Industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, ceramics, and even metal processing leverage silicon carbide heating elements for efficient heating solutions. Their robust nature not only ensures longevity but also reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby lowering operational costs.
One of the primary benefits of silicon carbide heating elements is their energy efficiency. They provide rapid heating and cooling capabilities, which optimize production cycles and minimize energy loss during operation. Additionally, they exhibit excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing them to perform reliably under extreme temperature variations. This characteristic is particularly valuable in applications where materials are exposed to sudden temperature changes. Moreover, silicon carbide elements are less prone to oxidation compared to other heating materials, providing enhanced performance in electric furnaces and kilns. As a result, they support more sustainable manufacturing processes by lowering energy consumption and extending equipment life.
When evaluating heating technologies, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements offer several distinct advantages over traditional heating solutions such as metal heating elements and electric resistance heaters.
One notable difference is the operating temperature range. Silicon carbide elements can withstand extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1,400°C, making them suitable for high-temperature applications where metals would degrade or oxidize. This resilience enables SiC elements to maintain performance and longevity in harsh environments and is particularly beneficial in industrial settings.
Additionally, silicon carbide heating elements exhibit superior energy efficiency. They possess rapid heating capabilities, allowing them to reach desired temperatures quicker than their metal counterparts. This efficiency not only reduces energy consumption but also minimizes heating cycles, leading to a more streamlined operational process. Moreover, SiC elements provide uniform heating, which is crucial for applications where consistent temperature distribution is needed to ensure product quality.
In comparison to ceramic or quartz heating technologies, silicon carbide offers additional thermal stability and mechanical strength. Ceramic heaters may be prone to chipping or cracking under thermal stress, while silicon carbide’s robust structure withstands thermal shock better. This durability translates into lower maintenance costs and improved reliability, making silicon carbide an increasingly popular choice in various industrial applications that demand consistent and high-performance heating solutions.