Leave Your Message
The Silicon Carbide Substrate has gained significant attention in recent years. This material, known for its superior thermal conductivity and electrical performance, is pivotal in modern electronic devices. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the Silicon Carbide market is projected to reach $5.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 17.5%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for efficient power electronics and high-temperature applications.
Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in semiconductor materials, states, “The Silicon Carbide Substrate is a game-changer for the industry.” The use of Silicon Carbide can lead to improved device efficiency and reduced energy consumption. However, despite its benefits, challenges remain. The manufacturing process for Silicon Carbide substrates is complex and costly. This may hinder widespread adoption, particularly in smaller companies.
Industries must assess the long-term advantages against initial investments. Not every application will benefit from Silicon Carbide. Innovative solutions in processing and technology may address these issues. Balancing costs and efficiency is essential for harnessing the full potential of Silicon Carbide Substrates.

Silicon carbide (SiC) substrates are gaining popularity in the semiconductor industry. They offer significant advantages over traditional silicon substrates. For instance, SiC can operate at high temperatures and voltages. This makes them ideal for power electronics. They are robust and efficient, which is essential for modern applications.
In addition to their thermal stability, silicon carbide substrates enhance device performance. They enable faster switching speeds in electronic devices. This can lead to smaller, more efficient power systems. However, working with SiC is not without challenges. The growing demand puts pressure on supply chains. The manufacturing process can also be complex.
One notable aspect is the cost considerations. Although prices have been decreasing, SiC remains more expensive than silicon. This could limit adoption in some markets. Still, the long-term benefits often justify the investment. As awareness grows, more industries are exploring SiC technologies. The potential is vast, but a cautious approach is necessary.
This chart illustrates the benefits of Silicon Carbide substrates across various performance metrics, highlighting their superior properties such as thermal and mechanical strengths that make them ideal for high-performance applications.
Silicon carbide (SiC) substrates have gained attention due to their unique composition and properties. SiC is a compound made from silicon and carbon. This structure gives it a high level of thermal conductivity. Additionally, it can withstand high temperatures and aggressive environments. These features make it an ideal substrate for high-power and high-frequency devices.
The physical properties of silicon carbide substrates enhance their appeal. They possess exceptional hardness and rigidity. This durability is useful in various applications, from electronics to automotive technologies. However, creating high-quality SiC substrates is not straightforward. The manufacturing process can be costly and complex. Companies often face challenges in achieving uniformity.
Moreover, SiC substrates offer advantages in efficiency. They allow for higher efficiency in energy conversion. This can lead to reduced energy loss in devices. However, the performance varies depending on the quality of the substrate. If impurities are present, the effectiveness can decrease significantly. As industries embrace SiC technology, refining these processes is essential.
Silicon carbide (SiC) substrates are changing the landscape of semiconductor technology. They offer remarkable thermal conductivity and a wide bandgap. This makes SiC ideal for high-temperature and high-voltage applications. In a world that's craving efficiency, SiC shines brightly. It allows for the miniaturization of components while enhancing performance.
One significant advantage of using silicon carbide is its high breakdown voltage. Devices can operate at higher voltages without failure. This leads to reduced energy loss and improved efficiency in power electronics. SiC also demonstrates impressive resistance to chemical corrosion. For industries that face harsh environments, this quality is invaluable. However, manufacturing SiC can sometimes be challenging and costly. Balancing cost and performance remains a topic of discussion among engineers.
Furthermore, SiC substrates have a unique capability to manage thermal dissipation. This results in devices that withstand extreme conditions without overheating. Yet, the growth of SiC wafers is not without its imperfections. Defects in the crystal structure can affect device performance. The semiconductor community is working diligently to address these issues. This ongoing research aims to fully unlock the potential of silicon carbide technology.
| Property | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Silicon (Si) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (up to 3.5 W/cm·K) | Moderate (1.5 W/cm·K) |
| Bandgap | Wide (3.0 eV) | Narrow (1.1 eV) |
| Breakdown Voltage | High (up to 10 kV) | Lower (around 500 V) |
| Temperature Range | High (above 600°C) | Lower (up to 200°C) |
| Efficiency in High Power Applications | Superior efficiency | Lower efficiency |
| Applications | Power electronics, RF devices | General electronics |
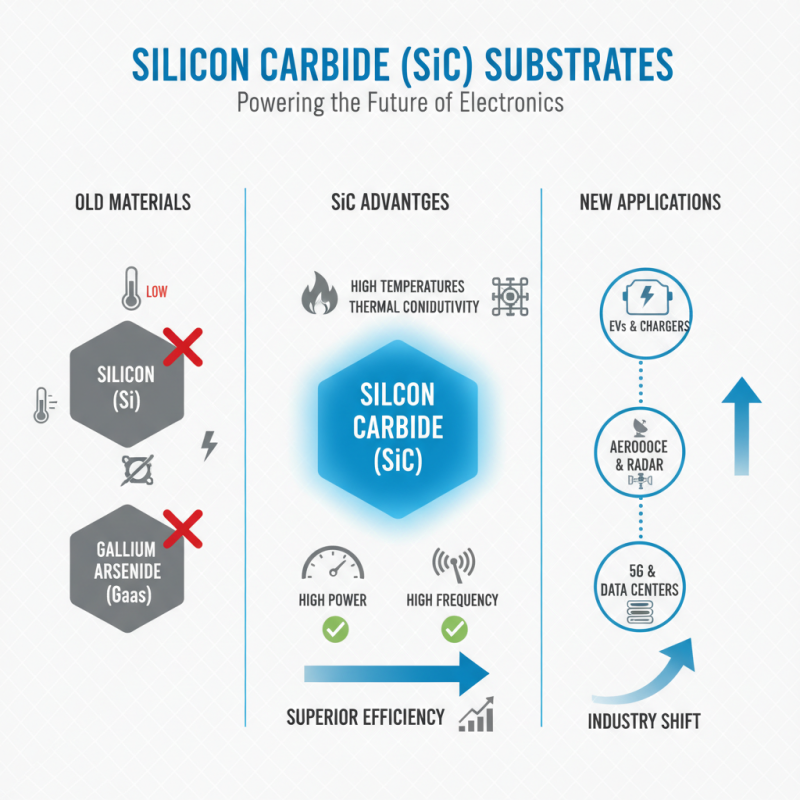
Silicon carbide (SiC) substrates are increasingly popular due to their unique properties. They outperform traditional substrate materials like silicon and gallium arsenide. SiC can endure high temperatures and has excellent thermal conductivity. This makes it ideal for high-power and high-frequency applications. Many industries are shifting towards SiC for its superior efficiency.
Compared to silicon, SiC can operate at higher voltages and frequencies. This results in smaller designs, which can save space and reduce costs. Gallium arsenide is another common substrate. However, SiC provides better thermal performance, which is crucial in demanding environments. Users may find SiC more reliable for long-term usage.
Tip: Consider your specific application requirements when choosing a substrate. Not all designs need the strengths of SiC, and sometimes, simpler options may suffice.
However, SiC substrates can be more expensive. This can be a barrier for some projects. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex. Careful consideration is necessary to weigh these factors against performance benefits.
Tip: Assess your budget and technical capabilities. Sometimes, starting with a simpler material may help refine your design before upgrading to more complex substrates like SiC.
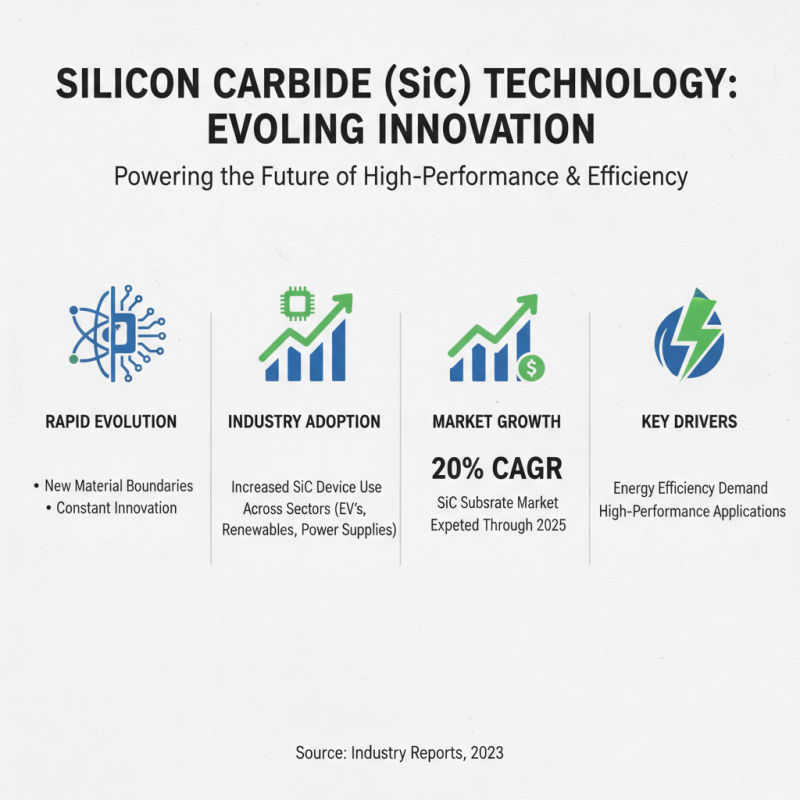
Silicon carbide (SiC) technology is rapidly evolving. Innovations are pushing the boundaries of this material in various sectors. Current industry trends show a significant increase in SiC device adoption. Reports indicate that the market for SiC substrates is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 20% through 2025. This growth is largely driven by the demand for energy efficiency and high-performance applications.
In the automotive and renewable energy sectors, SiC offers unique benefits. It can handle high voltages and temperatures better than traditional silicon. As electric vehicles (EVs) become mainstream, SiC will play a crucial role. Its ability to reduce energy loss in power electronics is a game-changer. Some studies suggest that SiC devices can achieve efficiencies above 98%. However, the high initial costs of SiC materials can be a barrier. This may cause some manufacturers to hesitate in making the switch.
Moreover, the integration of SiC in 5G technology is gaining traction. High-frequency performance makes it suitable for this application. Yet, challenges remain. The lack of standardized production processes can impact reliability. As the industry moves forward, ongoing research will be vital. Innovation in SiC fabrication and cost reduction strategies will shape its future. The potential is immense, but the execution needs to improve.






