Leave Your Message
Silicon steel, known for its magnetic properties, plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency across various electrical applications. Its unique composition, which includes a specific amount of silicon, significantly reduces energy loss during the transmission and transformation of electrical energy. As the demand for energy-efficient solutions grows, the adoption of silicon steel is becoming increasingly vital in industries ranging from power generation to electric vehicles. Understanding the advantages and applications of silicon steel can lead to more sustainable practices in the utilization of electrical energy.
In this discussion, we will explore the fundamental properties of silicon steel that contribute to its energy-efficient performance. We will delve into how these materials can be effectively integrated into electrical applications, such as transformers, motors, and generators, resulting in reduced operational costs and minimized energy waste. Additionally, the increasing shift towards renewable energy sources highlights the importance of incorporating advanced materials like silicon steel to harness energy more efficiently. Overall, leveraging silicon steel in electrical applications not only promotes operational excellence but also supports broader environmental sustainability goals.
Silicon steel, primarily composed of iron and silicon, is a critical material used in electrical applications due to its advantageous magnetic properties. With silicon content typically ranging between 1% to 6.5%, this alloy significantly enhances electrical resistivity and reduces hysteresis loss, making it ideal for transformers and electric motors. According to a recent industry report from the International Energy Agency, the use of silicon steel can lead to efficiency improvements of 0.5% to 2% in electrical devices, cumulatively saving substantial energy throughout their operational lifespan.
When working with silicon steel, it is essential to consider the alloy's crystalline structure, which influences its magnetic performance. The reduction in weight and energy loss associated with silicon steel compared to traditional carbon steel allows manufacturers to design lighter and more efficient electric machines. Tips for optimizing energy efficiency include ensuring precise control of the silicon content during the production process and utilizing advanced manufacturing techniques, such as grain-oriented electrical steel production, which aligns the crystalline structure to provide superior magnetic permeability.
Moreover, maintaining optimal processing conditions, such as temperature and cooling rates, can further enhance the final properties of the silicon steel. Proper heat treatment not only improves magnetic performance but also increases the overall durability of electrical components. As the demand for energy efficiency continues to rise, understanding and utilizing the properties of silicon steel becomes increasingly vital for engineers and manufacturers in the electrical industry.
| Property | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon Content | Typically 1-6% silicon by weight | Reduces hysteresis loss in magnetic applications |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate, improving with increasing silicon | Enhances energy efficiency in transformers and motors |
| Magnetic Permeability | High permeability, varies with heat treatment | Improves induction capability, reducing core losses |
| Mechanical Properties | Good ductility and strength | Facilitates processing and reduces handling damage |
| Heat Resistance | Stable up to certain temperatures | Minimizes performance degradation at elevated temperatures |
Silicon steel, particularly in its electrical grade form, has emerged as a cornerstone material for enhancing energy efficiency in various electrical applications. One of the primary advantages of silicon steel is its excellent magnetic properties, which significantly reduce energy losses. According to a report from the International Energy Agency, the inclusion of silicon in electrical steel can lower core losses by up to 50%, making it highly desirable for motors, transformers, and generators that operate continuously in high-efficiency environments. This enhancement directly contributes to lower operational costs and improved system performance.

Another key benefit of silicon steel lies in its ability to withstand higher temperatures without compromising performance. With an increase in energy demands and the need for sustainable solutions, electrical devices are increasingly pushed to operate under more strenuous conditions. Silicon steel grades with higher silicon content can maintain magnetic efficiency and structural integrity at elevated temperatures, ensuring longevity and reliability. A study published by the Electric Power Research Institute indicates that using silicon steel in transformer cores can lead to a significant reduction in energy consumption, contributing to an estimated annual savings of 15 billion kWh in the United States alone. This positions silicon steel as an indispensable material for industries striving towards energy-efficient practices.
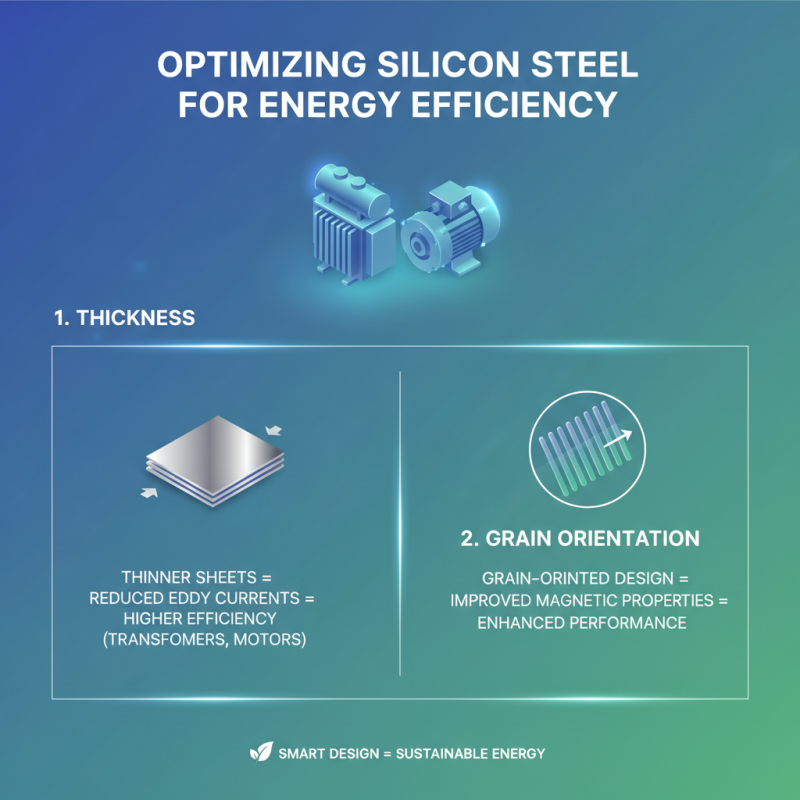
When designing components that utilize silicon steel, several key considerations must be addressed to optimize energy efficiency in electrical applications. One of the primary factors is the thickness of the silicon steel sheets. Thinner sheets can reduce energy losses due to eddy currents, making them ideal for applications like transformers and electric motors. Engineers should also take into account the orientation of the grain structure within the silicon steel, as performing a grain-oriented design can further improve magnetic properties and enhance performance.
Tips for maximizing the effectiveness of silicon steel components include ensuring proper lamination to minimize eddy current losses. This can be achieved by using insulated coatings between the layers, which helps maintain high performance over time. Additionally, selecting the right silicon content is crucial; varying levels between 2% to 6.5% can lead to different performance outcomes, enabling designers to choose the right balance between cost and efficiency.
Another important design consideration is the overall shape and size of the components. Optimizing the geometry of silicon steel parts can lead to a more uniform magnetic field, which is critical for devices such as inductors and transformers. Engineers should also consider the operational environment, as temperature fluctuations can impact the magnetic properties of silicon steel.

The advancement of energy efficiency in electrical applications is increasingly reliant on the implementation of silicon steel, a material known for its superior magnetic properties. According to the International Energy Agency, transformers account for approximately 40% of energy losses in electrical systems, emphasizing the necessity of optimizing material choices. Silicon steel, with its reduced hysteresis loss compared to conventional steel, can help lower these energy losses significantly, enhancing overall system performance.
One effective strategy for implementing silicon steel is through the design of core components in electrical devices. By utilizing high-grade silicon steel with specific grain-oriented structures, manufacturers can reduce eddy current losses, which are critical in applications such as power transformers and electric motors. A report from the U.S. Department of Energy highlights that using high-efficiency silicon steel can lead to a 10-15% improvement in energy use in power transformers alone. Additionally, the integration of advanced manufacturing techniques and precision engineering can further optimize the alignment and thickness of silicon steel sheets, resulting in even higher efficiency gains.
Incorporating energy-efficient design practices not only enhances the performance of electrical applications but also aligns with global sustainability goals. The adoption of silicon steel contributes to lower carbon footprints in energy systems. A study by the European Commission indicates that enhancing the energy efficiency of electrical equipment could lead to savings of over 300 terawatt-hours annually by 2030, showcasing the significant potential for silicon steel use across various sectors.
The demand for silicon steel in electrical systems is poised to grow significantly, driven by the increasing need for energy-efficient solutions in various applications. Recent reports from industry analysts indicate that the global market for silicon steel is expected to reach approximately $40 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6% from 2020. This growth is largely attributed to the heightened emphasis on reducing energy consumption in electrical devices, which requires high-performance materials such as silicon steel that minimize energy losses during operation.
Future trends indicate a shift towards advanced manufacturing techniques and innovative alloy compositions that enhance the magnetic properties of silicon steel, thus further improving energy efficiency. Research suggests that specialized silicon steel grades, designed for specific applications like electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, will dominate the market. The International Energy Agency estimates that implementing high-grade silicon steel in electrical transformers can lead to energy savings of up to 50%, underscoring its critical role in achieving global energy efficiency targets.
As industries continue to adopt these cutting-edge materials, the evolution of silicon steel within electrical systems will pave the way for more sustainable and efficient technologies.






