Leave Your Message
In recent years, the application of Silicium Carbide (SiC) has garnered significant attention within the semiconductor industry, primarily for its potential to enhance performance and efficiency in various electronic devices. As the demand for energy-efficient technologies grows, experts suggest that SiC has become a crucial material in the quest for improved performance metrics. Dr. Emily Renard, a leading figure in semiconductor research, once noted, "Silicium Carbide is not just a material; it is a game changer for high-performance applications that require both durability and efficiency."
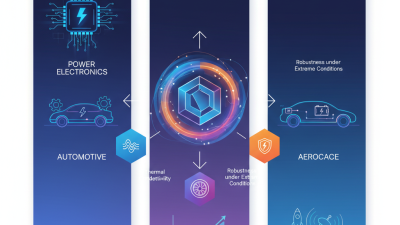
The versatility of Silicium Carbide allows it to be utilized in a variety of applications, from power electronics to electric vehicles. Its unique properties, including a higher thermal conductivity and a wider bandgap compared to traditional silicon, position SiC as an invaluable resource in pushing the boundaries of what is technologically possible. As industries strive for advancements in sustainability and performance, the integration of Silicium Carbide into their operations represents a pivotal step toward achieving these goals. This article will explore the myriad ways in which Silicium Carbide can be effectively utilized to optimize performance and efficiency across diverse sectors, setting the stage for a more technologically advanced future.

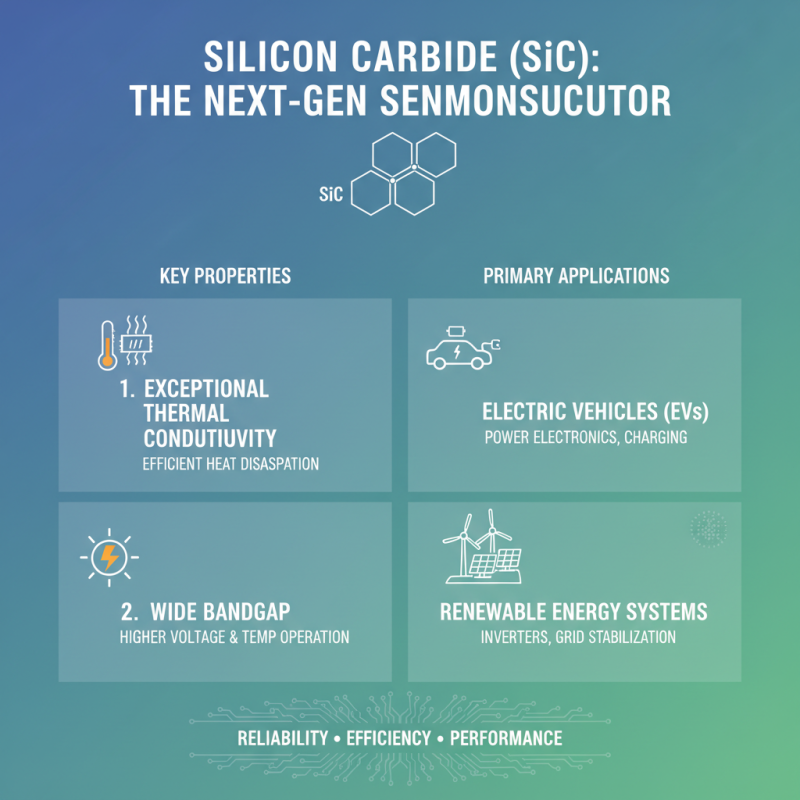
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound semiconductor that has gained considerable attention for its unique properties and advantages in various applications. One of its most significant characteristics is its remarkable thermal conductivity, which makes it highly efficient in heat dissipation. This property is essential in high-power and high-frequency applications, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, where managing heat is critical for performance and reliability. Additionally, SiC exhibits a wide bandgap, enabling devices made from this material to operate at higher voltages and temperatures compared to conventional semiconductors like silicon.
Another advantage of silicon carbide is its exceptional hardness, which contributes to its durability and longevity in harsh environments. This toughness makes SiC an ideal choice for applications where mechanical stress and thermal fluctuations are prevalent, such as aerospace, industrial machinery, and power electronics. Furthermore, its chemical stability and resistance to oxidation enhance its applicability in corrosive environments, increasing the lifespan of components and reducing maintenance costs. Together, these properties position silicon carbide as a superior material for advancing technology in a variety of industries, driving enhanced performance and efficiency.
Silicon carbide (SiC) has emerged as a revolutionary material in various technological applications, especially in high-performance devices. Its exceptional thermal conductivity and wide bandgap make it ideal for power electronics, enhancing efficiency in applications ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems. SiC components can operate at higher voltages and temperatures compared to traditional silicon, leading to smaller, lighter devices and improved energy management.
In the realm of semiconductors, silicon carbide is used in power transistors and diodes that significantly boost the efficiency of energy conversion. This is crucial in sectors like telecommunications, where SiC is employed in RF amplifiers to improve signal quality and efficiency. Moreover, the adoption of SiC in electric vehicles enables faster charging and extended range, which contributes to the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
Tips: When considering SiC for your projects, ensure to evaluate its operating conditions to maximize its benefits. Additionally, collaborating with experts during the design phase can lead to innovative implementations that fully utilize the properties of silicon carbide. Keep an eye on emerging trends and advancements in SiC technology, as this will help you stay ahead in optimizing your applications for better performance and efficiency.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Future Prospects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Electronics | Used in semiconductor devices for better thermal conductivity. | Higher efficiency, reduced size and weight, improved thermal management. | Increased adoption in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. |
| LED Technology | Utilized in high-performance LED lighting systems. | Longer lifespan, higher brightness, lower energy consumption. | Expansion in various lighting applications and smart lighting solutions. |
| Aerospace Components | Application in structural components of aerospace systems. | Lightweight, strong, and able to withstand high temperatures. | Potential for broader adoption in commercial and military aircraft. |
| Electric Vehicles | Incorporated in battery management systems and drivetrains. | Enhanced range, faster charging, improved overall performance. | Growing market as EV adoption accelerates worldwide. |
| Renewable Energy Systems | Used in inverters for solar power generation. | Higher efficiency in power conversion, better resilience to harsh conditions. | Expected growth with increasing global energy transition efforts. |
Silicium carbide (SiC) has emerged as a game-changer in various manufacturing processes, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and power electronics. Its remarkable thermal conductivity, high breakdown voltage, and superior hardness make it an ideal choice for enhancing performance and efficiency in various applications. Recent reports from the Semiconductor Industry Association indicate that the SiC market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 25.9% from 2021 to 2025, underscoring its increasing adoption in high-efficiency devices.
Integrating SiC into manufacturing processes requires a clear understanding of its properties and the techniques available for its implementation. One effective approach is to utilize SiC substrates in power electronics fabrication, which significantly improves energy efficiency and switch speed. This technique not only reduces thermal management requirements but also enhances the longevity of devices. Moreover, advancements in wafer fabrication have led to the production of larger SiC wafers, which in turn lower the overall manufacturing costs and improve yield rates.
Tips:
When considering SiC integration, ensure to invest in training for your engineering team on the unique machining and bonding characteristics of SiC. Additionally, collaborating with material scientists can lead to innovative applications that maximize the advantages of SiC in your specific manufacturing context. Exploring partnerships with academic institutions for research and development can also pave the way for discovering new uses of SiC technology, further enhancing your competitive edge.

Silicon carbide (SiC) is rapidly becoming a preferred material in various industries due to its exceptional efficiency and performance advantages over traditional silicon. However, incorporating silicon carbide into existing systems presents a set of challenges that can hinder its widespread adoption. One significant challenge is the relatively high cost of SiC substrates compared to silicon. This can deter manufacturers from making the switch despite the long-term benefits associated with enhanced thermal conductivity and energy efficiency. Additionally, the production of SiC devices requires specialized techniques that some manufacturers may not yet possess.
To address these challenges, one solution is to invest in advanced manufacturing technologies that can lower production costs and increase yield. By developing more efficient methods for creating SiC substrates and devices, companies can make the material more accessible. Collaboration between academia and industry could also drive innovation in this area, creating shared resources for research and development to overcome the hurdles of SiC integration.
Tips for successfully transitioning to silicon carbide include conducting thorough market analyses to identify potential savings on energy and performance over time. It’s also advisable to initiate pilot projects to test the scalability of SiC technologies before a full rollout. Collaborating with experienced suppliers can provide insights into best practices and help mitigate risks associated with implementation. Exploring hybrid solutions that combine silicon and silicon carbide may also ease the transition while maximizing benefits.
As the demand for more efficient and durable components continues to rise, Silicium Carbide (SiC) technology is at the forefront of innovation across various industries, particularly in automotive and power electronics. Recent reports suggest that the SiC semiconductor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 20% through 2025, driven by the increasing need for improved thermal conductivity and efficiency in high-performance applications. The material’s ability to operate at higher temperatures and voltages positions it as a game-changer in the development of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy systems.
Companies investing in SiC technology are focusing on innovations that enhance its performance. Enhanced manufacturing processes are being developed to reduce defects in SiC wafers, which can significantly improve overall efficiency. For instance, advancements in crystal growth techniques are leading to higher yield rates and better material quality, essential for producing reliable semiconductor devices. Additionally, the integration of SiC in power modules is facilitating greater energy savings, with estimates stating that systems utilizing SiC can achieve up to 50% lower losses compared to traditional silicon counterparts.
Tips: To maximize the benefits of SiC technology, industry stakeholders should consider collaborating with research institutions focused on material science to stay ahead of emerging trends. Furthermore, conducting regular assessments of production techniques can help identify areas for improvement and innovation, ensuring that companies remain competitive in this rapidly evolving market.
This chart illustrates the projected trends for efficiency improvement and performance enhancement attributed to the advancements in Silicium Carbide technology from 2023 to 2025. The data indicates a significant upward trend, showcasing the potential impact of these innovations in various applications.