Leave Your Message
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern industry, the integration of advanced materials plays a pivotal role in enhancing performance and efficiency. One such material that has garnered significant attention is Silicon Iron. Renowned for its superior magnetic properties, Silicon Iron has become a cornerstone in the production of high-efficiency electrical components, revolutionizing sectors such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. Dr. James Whittaker, a leading expert in materials science at the Institute for Advanced Industrial Research, emphasizes the potential of Silicon Iron, stating, "The unique properties of Silicon Iron not only improve the performance of electrical applications but also contribute to the sustainability goals of modern manufacturing."
As industries strive for innovation and competitiveness, the utilization of Silicon Iron is proving to be a game-changer. Its ability to enhance electromagnetic performance while reducing power losses makes it an ideal choice for transformers and electric motors. The transition towards using Silicon Iron in various applications aligns with the global commitment to developing cleaner and more efficient technologies. By harnessing the power of Silicon Iron, industries can not only optimize their operational efficiency but also work towards a more sustainable future, ultimately shaping the landscape of modern industrial practices.

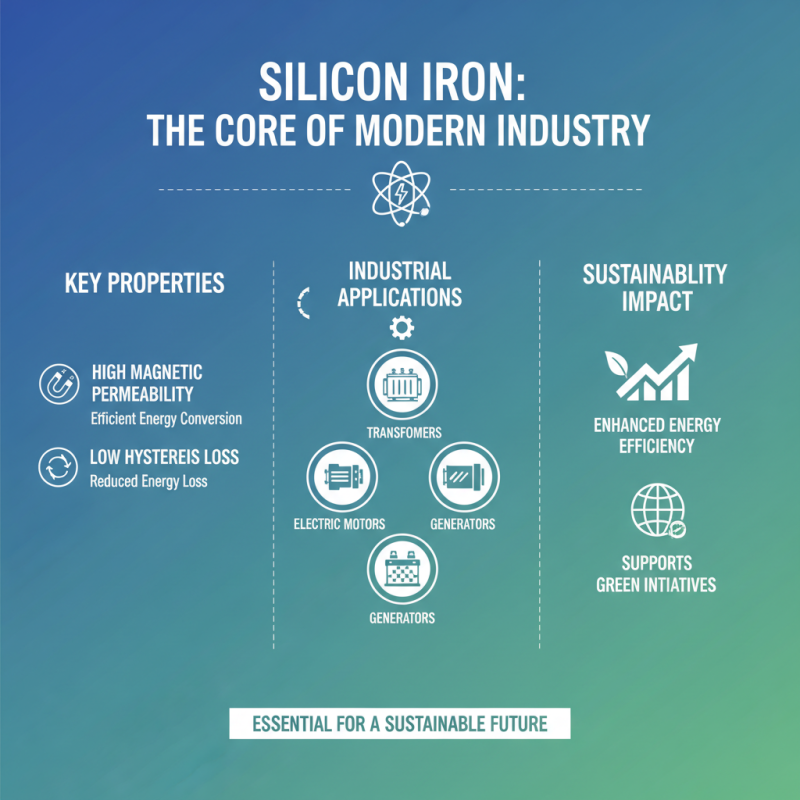
Silicon iron, an alloy composed primarily of iron and silicon, has become an essential material in various industrial applications due to its unique properties. One of the most significant characteristics of silicon iron is its magnetic permeability, which enhances its performance in electromagnetic devices. This property allows for efficient energy conversion and reduced energy losses, making silicon iron a popular choice for the production of transformers, electrical motors, and generators. Additionally, its low hysteresis loss contributes to better energy efficiency in these applications, thereby supporting the growing demand for sustainable industrial practices.
The benefits of silicon iron extend beyond its magnetic properties. The alloy exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, which are crucial for components that operate in challenging environments. This durability not only prolongs the lifespan of industrial equipment but also reduces maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective solution for manufacturers. Moreover, silicon iron can be easily processed into various shapes and sizes, allowing for flexibility in design and application. As industries increasingly seek materials that provide both performance and reliability, silicon iron stands out as a valuable resource, driving advancement in modern engineering and technology.
Silicon iron, an alloy of iron with silicon, has become increasingly vital in electrical engineering and machinery due to its unique properties. In the realm of electrical engineering, silicon iron is primarily used in the production of transformer cores and electric motor laminations. The addition of silicon enhances magnetic permeability while reducing energy losses through hysteresis and eddy currents. This property makes silicon iron an ideal material for components that require efficient energy conversion and minimal heat generation, which is essential for modern electrical devices and systems.
In machinery, silicon iron components play a pivotal role in improving the performance and durability of various mechanical systems. Its high tensile strength and corrosion resistance make it suitable for applications in automotive engines, generators, and other industrial machines. The lightweight nature of silicon iron, combined with its mechanical robustness, allows engineers to design more efficient machines that can operate at higher speeds and loads without compromising structural integrity. This versatility positions silicon iron as a key material in the advancement of both electrical and mechanical engineering, supporting the ever-growing demands of modern industrial applications.
Silicon iron has emerged as a powerful alternative to traditional steel alloys in various industrial applications, thanks to its unique composition and properties. When comparing silicon iron to traditional steel alloys, one critical advantage lies in its enhanced magnetic properties. Silicon iron exhibits lower energy losses when subjected to magnetic fields, making it an ideal choice for electrical applications, such as transformers and motors. Traditional steel alloys, while strong, often fall short in efficiency due to higher core losses, which can impact overall performance.
Tips: When transitioning to silicon iron from traditional steel alloys, ensure you evaluate the specific requirements of your application. Conducting a thorough analysis of magnetic performance can help determine the optimal silicon content, which typically ranges between 3% to 5%. This not only maximizes efficiency but also minimizes energy loss.
Another comparative factor is the temperature resistance of silicon iron. Silicon iron alloys maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures, surpassing many conventional steel options. This attribute not only allows for greater design flexibility but also enhances the durability of components exposed to high thermal environments.
Tips: During the design phase, consider the operating temperature range of your application. Implementing silicon iron can lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer service life due to its improved thermal stability.
When processing and fabricating silicon iron components, several best practices can greatly enhance performance and efficiency. First, it is essential to select the appropriate silicon content based on the specific application requirements. Typically, silicon content between 1% and 6% can offer a sweet spot for magnetic core applications, improving hysteresis loss and core efficiency. Careful consideration of alloying elements, such as aluminum or phosphorus, can further optimize the material properties and enhance its performance in demanding environments.
Another critical aspect of fabricating silicon iron components is employing suitable shaping techniques. Techniques such as cold working and heat treatment are vital in achieving desired mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy. Cold working helps in increasing the strength of the material, while controlled heat treatment can relieve internal stresses and improve ductility. Additionally, precision machining and surface treatments can enhance the durability and performance of the silicon iron components, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of modern industrial applications.
Thorough quality control measures should also be in place throughout the processing stages. Conducting regular inspections and utilizing advanced testing methods can help identify potential issues early, ensuring that the final components meet the stringent quality standards required in modern manufacturing environments. By adhering to these best practices, manufacturers can effectively harness the advantages of silicon iron in their products, resulting in enhanced performance and reliability.
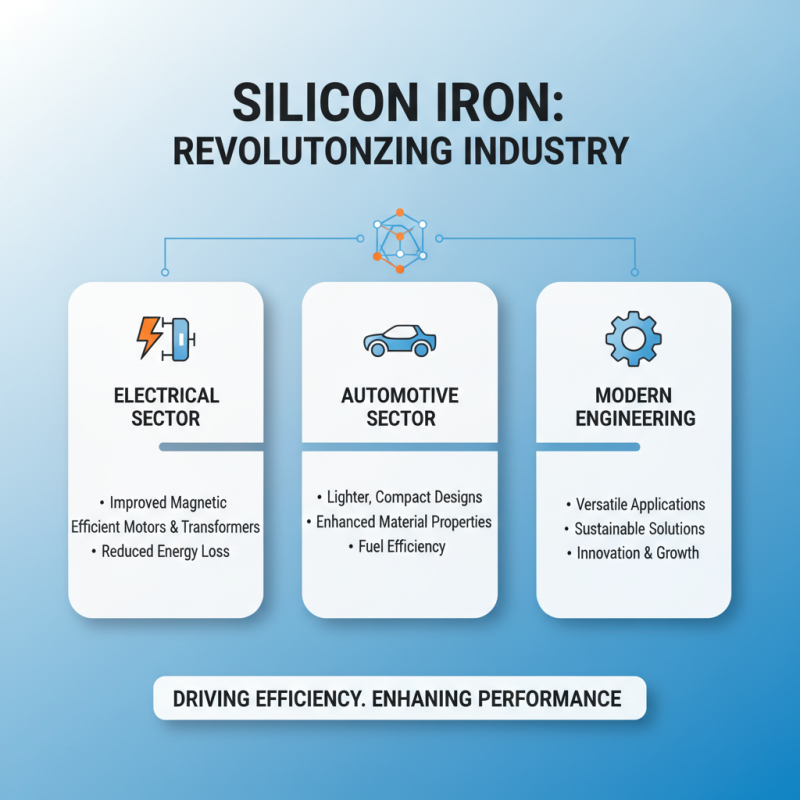
The utilization of silicon iron in various industries is rapidly evolving, driven by the demand for increased efficiency and enhanced material properties. In the electrical and automotive sectors, innovations in the alloy's composition are enabling manufacturers to produce components that exhibit superior magnetic performance, leading to more efficient motors and transformers. This shift towards silicon iron not only aids in reducing energy losses but also supports the development of lighter and more compact designs, making it an attractive option for modern engineering challenges.
Looking ahead, the future trends in silicon iron usage appear promising. Researchers are exploring advanced processing techniques and the integration of silicon iron with other materials to optimize its properties further. The growing emphasis on sustainability is also influencing innovation, with the potential for recycled silicon iron materials playing a significant role in reducing industrial waste. As industries continue to adapt to stricter environmental regulations, the evolution of silicon iron stands poised to contribute significantly to both performance enhancements and ecological sustainability across a wide range of applications.






